Caffeine is the world’s most widely consumed psychoactive substance, found in coffee, tea, energy drinks, and even some medications. For many, it’s an essential part of their daily routine, providing that much-needed energy boost and mental alertness. But have you ever wondered how caffeine affects your body, beyond the immediate jolt of wakefulness it provides?
Page Contents
In this blog, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of caffeine, exploring its effects on various body systems, discussing its perks, and highlighting some potential pitfalls. By the end, you’ll have a deeper understanding of the complex relationship between caffeine and your body.
The Basics of Caffeine
Before we dive into the intricate details of caffeine’s impact, let’s start with the basics. Caffeine is a natural stimulant that belongs to a group of compounds known as xanthines. It’s primarily found in coffee beans, tea leaves, cocoa beans, and some other plants. Here’s how it works:
Blocking Adenosine: In your brain, there’s a neurotransmitter called adenosine, which accumulates over the course of the day, making you feel tired and drowsy. Caffeine is structurally similar to adenosine, which allows it to bind to the same receptors. By doing so, caffeine blocks the adenosine receptors, reducing the feeling of fatigue and increasing alertness.
Releasing Neurotransmitters: Caffeine also stimulates the release of other neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine. These chemicals play a role in mood, focus, and overall brain function. That’s why caffeine can make you feel more awake and, in some cases, happier.
Read also : 10 Surprising Health Benefits of Dark Chocolate
Now, let’s take a closer look at how caffeine affects your body:
How Caffeine Affects Your Central Nervous System
The most obvious and immediate impact of caffeine is on your central nervous system. As mentioned earlier, it blocks adenosine receptors, preventing the feeling of drowsiness. This effect can vary from person to person, depending on their sensitivity to caffeine and how much they consume. Some individuals may feel a surge of energy with just one cup of coffee, while others may require several cups to experience the same effect.
Caffeine also has an impact on cognitive functions. It can improve alertness, concentration, and overall mental clarity. This is why many people rely on that morning cup of coffee to kickstart their day. However, excessive caffeine intake can lead to restlessness, anxiety, and even insomnia in some individuals.
The Cardiovascular System and Caffeine
Your cardiovascular system is another area where caffeine makes its presence felt. While moderate caffeine consumption can have some benefits, such as increasing heart rate and potentially improving blood flow, excessive consumption can lead to issues. Let’s explore both sides of the coin.
Benefits: Caffeine can stimulate your heart, causing an increase in heart rate and, in some cases, a mild increase in blood pressure. This can be beneficial in certain situations, like improving alertness during long drives or enhancing athletic performance. Some studies even suggest that moderate caffeine consumption may be associated with a reduced risk of heart disease.
Potential Pitfalls: On the flip side, if you consume too much caffeine, it can lead to irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) or exacerbate pre-existing heart conditions. It’s essential to know your own tolerance and consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns about caffeine’s impact on your heart.
Caffeine’s Effects on Metabolism and Weight Management
Caffeine also influences your body’s metabolic processes. It can have both positive and negative effects on your weight and overall metabolism.
Positive Effects: Caffeine is a common ingredient in many weight-loss supplements. It’s believed to increase metabolic rate, encouraging the body to burn more calories. This is why it’s often touted as a fat-burning aid. Additionally, caffeine can enhance physical performance by releasing fatty acids from fat tissues, which can be used as a source of energy.
Potential Pitfalls: While caffeine can be beneficial for weight management, it’s not a magic bullet for shedding pounds. Moreover, relying solely on caffeine for weight loss can lead to negative side effects like jitteriness, insomnia, and gastrointestinal disturbances. It’s important to remember that a balanced diet and regular exercise are the cornerstones of a healthy lifestyle.
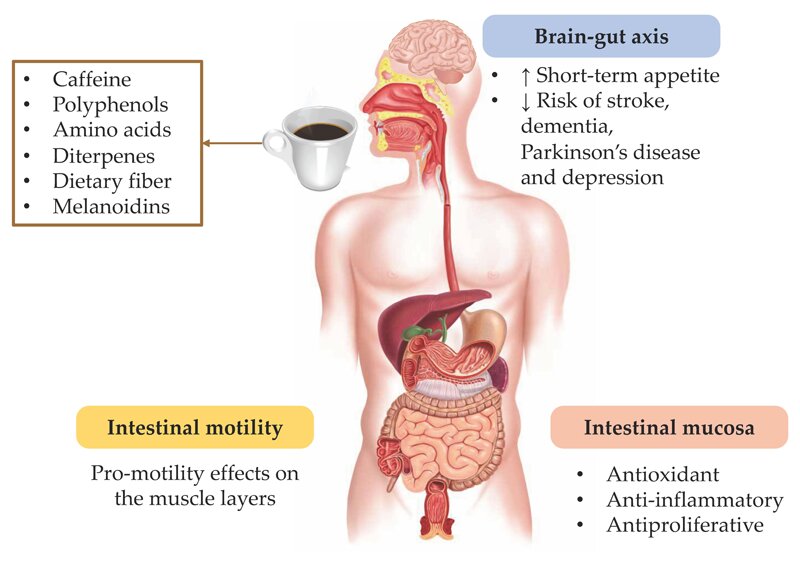
The Impact on Digestive System
Caffeine can also influence your digestive system. Many people find that a cup of coffee can help get things moving, so to speak. This effect is primarily due to its ability to stimulate the muscles in your digestive tract. However, it’s a double-edged sword.
Benefits: If you struggle with constipation, a cup of coffee can provide much-needed relief. Caffeine acts as a natural laxative, helping to stimulate bowel movements. It can also relax the lower esophageal sphincter, potentially reducing the risk of acid reflux.
Potential Pitfalls: For some individuals, caffeine can irritate the stomach lining, leading to discomfort, acid reflux, or gastritis. Excessive caffeine intake, especially on an empty stomach, can exacerbate these issues. It’s important to be mindful of your body’s response and limit consumption if you experience gastrointestinal discomfort.
Caffeine’s Influence on Mood and Mental Health
Beyond its physiological effects, caffeine has a significant impact on mood and mental health. Many people use caffeine to lift their spirits and stay more alert during the day.
Benefits: Caffeine can enhance mood by increasing the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine, which are associated with feelings of pleasure and alertness. It can also help in reducing the risk of depression and may improve cognitive function in the short term.
Potential Pitfalls: On the downside, excessive caffeine consumption can lead to anxiety, jitteriness, and even panic attacks in some individuals. It can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia, which can further worsen mood and mental health. People with certain anxiety disorders or sleep issues may need to be particularly cautious with their caffeine intake.
The Effect of Caffeine on Sleep
Sleep is crucial for overall health and well-being, and caffeine can significantly impact your ability to get a good night’s rest.
Benefits: In moderation, caffeine can help individuals stay awake and alert during the day, which is particularly helpful when dealing with demanding work schedules or jet lag. For some people, it can even enhance their productivity and focus.
Potential Pitfalls: However, caffeine has a long half-life, meaning it can stay in your system for hours, leading to disrupted sleep patterns. Consuming caffeine too close to bedtime can make it difficult to fall asleep or stay asleep throughout the night. Chronic sleep disruption can have a negative impact on your physical and mental health.
Read Also : 10 Surprising Health Benefits of Drinking Green Tea
Caffeine and Tolerance
One intriguing aspect of caffeine is its ability to induce tolerance in regular users. Tolerance occurs when the body becomes less responsive to a substance, leading individuals to consume more of it to achieve the same effects. Over time, this can lead to an increased dependence on caffeine.
If you’re a regular caffeine consumer, you may have noticed that your body has adapted to its presence. That’s because your brain responds to the chronic blockade of adenosine receptors by producing more adenosine receptors. This means you need more caffeine to achieve the same level of alertness. However, there are potential downsides to this adaptation:
Withdrawal Symptoms: If you suddenly reduce or eliminate your caffeine intake, you might experience withdrawal symptoms like headaches, irritability, and fatigue. These symptoms can make it challenging to quit or cut back on caffeine.
Increased Tolerance: The more caffeine you consume, the higher your tolerance becomes. This can lead to a vicious cycle of increasing caffeine intake, which may result in negative health consequences.
Safe Caffeine Consumption Guidelines
Now that we’ve explored the diverse ways caffeine can affect your body, let’s discuss some guidelines for safe caffeine consumption:
Know Your Limit: Everyone’s tolerance to caffeine is different. Pay attention to how your body responds, and stick to an amount that doesn’t cause negative side effects like jitteriness, anxiety, or sleep disturbances.
Stay Hydrated: Caffeine is a diuretic, which means it can increase urination and potentially lead to dehydration. Counteract this effect by drinking water regularly.
Avoid Caffeine Close to Bedtime: To protect your sleep, try to avoid caffeine in the hours leading up to bedtime. This will give your body a chance to clear the caffeine from your system and improve your sleep quality.
Moderation is Key: Enjoy caffeine in moderation, ideally as part of a balanced diet. Avoid relying on it as your sole source of energy.
Consider Individual Factors: Keep in mind that certain medical conditions, medications, and genetic factors can influence how your body responds to caffeine. If you have concerns, consult with a healthcare professional.
Conclusion
Caffeine is a fascinating compound with both perks and pitfalls. When consumed in moderation, it can provide a welcome boost in energy, mood, and cognitive function. However, excessive or irresponsible caffeine intake can lead to a range of negative side effects, from anxiety and sleep disturbances to gastrointestinal issues and cardiovascular problems.
Understanding how caffeine affects your body and being mindful of your consumption is key to enjoying its benefits while avoiding its downsides. Remember that individual tolerance varies, and what works for one person may not work for another. By staying informed and listening to your body, you can make informed choices about your caffeine intake and maintain a healthier, more balanced lifestyle.


